STRATEGY FORMULATION:
CUSTOMER INTERFACE
Introduction
*Customer interface
– Is the virtual representation of a firm’s chosen value proposition
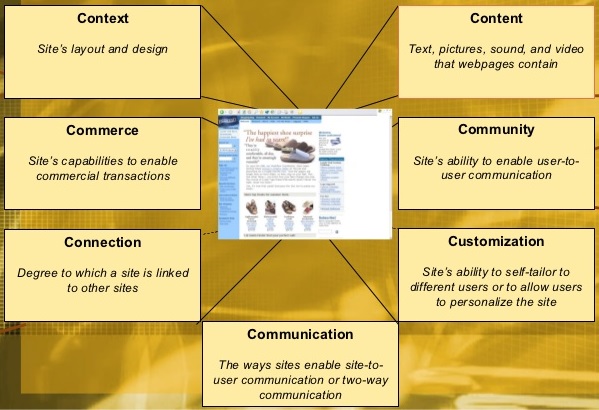
Seven design elements of the customer interface (7Cs):
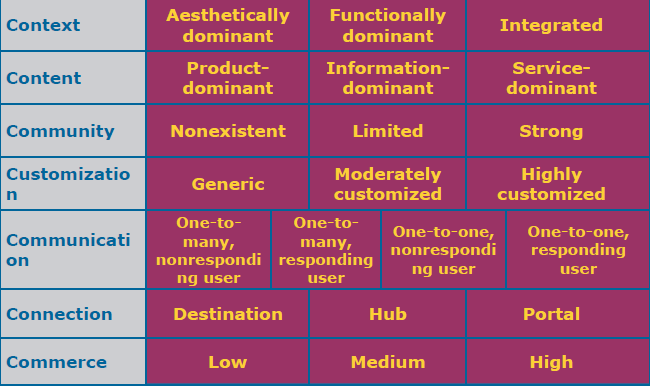
1. Context
2. Content
3. Community
4. Customization
5. Communication
6. Connection
7. Commerce
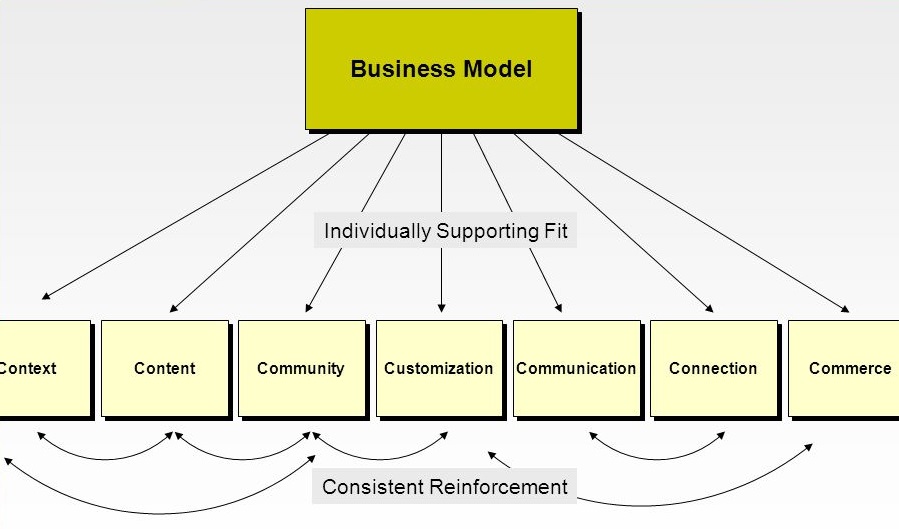
The 7Cs of Customer Interface
Fit & Reinforcement of the 7Cs
Context: The Determinant the Look-and-Feel of the Design
*Context of a website
– Captures its aesthetics and functional look-and-feel
*Function
– Refers to the organization and accessibility of information
Dimensions of Context:
a. Section Breakdown
b. Linking Structure
c. Navigation Tools
d. Speed
e. Reliability
f. Platform Independence
g. Media Accessibility
*Aesthetics
– Refers to the visual characteristics of a site
*Color Scheme
*Visual Themes
Context Classifications
1. Aesthetically Dominant: Emphasis is on the look-and-feel of the site.
2. Functionally Dominant: Emphasis is on the display of textual information.
3. Integrated: Balance of form and function.
Form versus Function (The Design Context Frontier)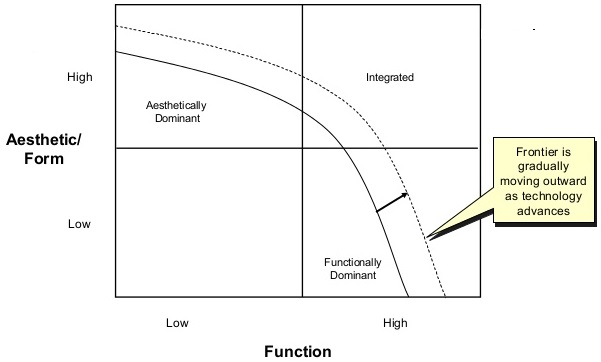
Content: Deciding What Information to Include
*Content of a website
– Refers to all the digital information on the site
Dimensions of Content:
– Offering Mix
– Appeal Mix
– Multimedia Mix
– Timeliness Mix (Current Content, & Reference Content)
Content Classifications:
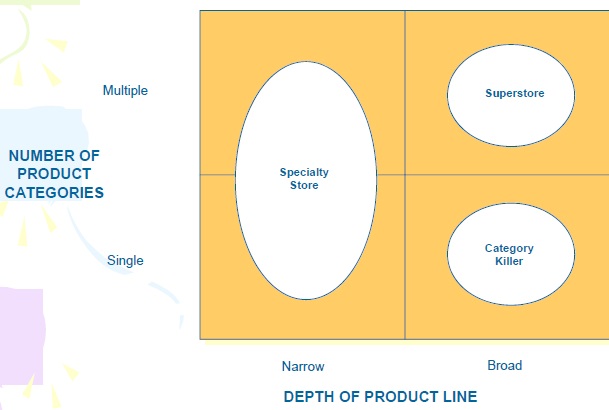
1. Product Dominant
– Encompasses store sites that primarily sell physical goods
*Superstore
*Category Killer
*Specialty Store
2. Information Dominant
– Encompasses store sites that focus heavily on information
3. Service Dominant
– Encompasses store sites that focus on the services offered, often for a fee
A Framework to Understand Content Classifications
What Makes a Community?
*Community
– Includes a feeling of membership in a group along with a strong sense of involvement and shared common interests
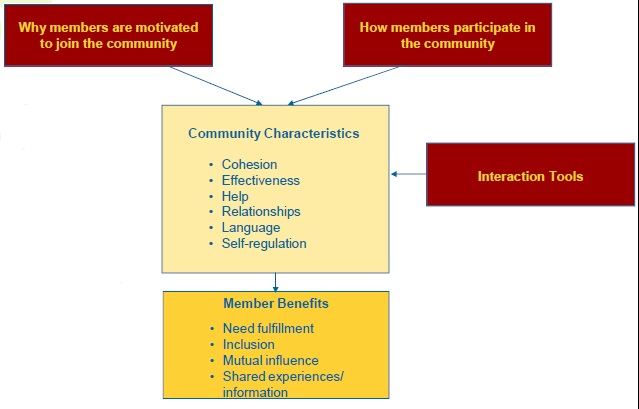
Five components determine the shape of online communities:
1. Characteristics
2. Member Motivation
3. Member Participation
4. Member Benefits
5. Interaction Tools
Characteristics
The more evolved the community the more likely it is to have these six characteristics:
1. Cohesion– the community develops a group identity
2. Effectiveness– the group has impact on members’ lives
3. Help– members feel comfortable asking for and receiving help from other members
4. Relationships– interaction between individuals leads to friendships
5. Language– members develop a specialized language and/or abbreviations with unique meaning within the community
6. Self-regulation– the group sets rules for its own interaction and develops a system for policing itself
Communities – Elements, Types, & Benefits
Community Classifications
1. Nonexistant– sites that have no community offer no way for users to interact with one another, on either a one-to-one basis or one-tomany basis
2. Limited– sites that offer features such as reading and posting information, stories, or opinions
3. Strong– sites that offer interactive community functions such as chat rooms and message boards
Customization: Creating an Individualized Website
*Customization
– Refers to a site’s ability to tailor itself to each user or to be tailored by the user
Dimensions of Customization:
1. Personalization: The user initiates and manages the customization process
2. Tailoring: Software dynamically publishes unique versions of the site to address specific user’s interests, habits and needs more appropriately
Commonly used customization features:
– E-mail accounts
– Content and layout configuration
– Storage
– Agents
Communication: Keeping in Touch with Users
*Communication
– Refers to the dialogue between a site and its users
Dimensions of Communication:
– Broadcast
– Interactive
Communication Archetypes:
1. One-to-Many, Non-Responding User
– Site messages are announcements that users receive without needing to respond.
2. One-to-Many, Responding User
– Site messages are invitations to users to submit their comments and responses.
3. One-to-One, Non-Responding User
– User receives personalized messages to address specific interests or needs without a need to respond.
4. One-to-One, Responding User
– User responds to personalized messages sent by the site.
Connection: Linking with Other Websites
*Connection
– Is the degree to which a given site is able to link to other sites
Dimensions of Connection:
– Outside Links
– Framed Links
– Pop-Up Windows
– Outsourced Content
Connections Classifications
1. Destination Site
– Provides almost exclusively site-generated content with very few links to other sites
2. Hub Site
– Provides a combination of sitegenerated content and selective links to sites of related interests
3. Portal Site
– Consists almost exclusively of links to a large number of other sites
Commerce: Enabling Financial Transactions
*Commerce
– Refers to the sale of goods, products or services on the site.
*Dimensions of Commerce
– Functional tools that are the commerceenabling features of a website
1. One-Click Shopping
2. Credit-Card Approval
3. Delivery Options
4. Security
5. Order Tracking
6. Shopping Cart
7. Configuration Technology
8. Registration
9. Orders Through Affiliates
Commerce Classifications:
1. Low
– These websites have the ability to process transactions, but with few of the tools that enable e-commerce.
2. Medium
– Some websites have no need for all the commerce bells and whistles and contain financial transactions as a necessary feature but not as their main purpose.
3. High
– These websites are fully equipped with all or almost all the functional tools that enable e-commerce.